Port Electrification Accelerates in 2025: A Global Shift Towards Greener Shipping
The maritime industry is undergoing a fundamental transformation in 2025, as major ports around the world are advancing their electrification strategies to align with global sustainability goals. Port electrification—where ports install infrastructure to connect ships directly to onshore power grids—is becoming a vital step toward reducing carbon emissions, noise pollution, and overall environmental impact.
May 2025 has witnessed significant developments from the Port of Bilbao in Spain, HAROPA PORT in France, and a strategic partnership in Singapore between Yinson GreenTech and Wilhelmsen Ships Service. These initiatives represent a broader trend that is setting the stage for a greener and smarter shipping industry by 2030.
Port of Bilbao: €50 Million Investment in Shore Power Infrastructure
The Port of Bilbao is moving full speed ahead with the second phase of its electrification journey. In May 2025, the Bilbao Port Authority’s Board approved a substantial investment of €50 million (approximately US$57 million) to develop advanced electrical infrastructure that will enable ships to plug into the local power grid.
This initiative is a continuation of Bilbao’s strategic commitment to decarbonize its port operations. By allowing vessels to connect to the shore power supply, the port significantly reduces reliance on diesel generators while docked—a known contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and poor air quality in port cities.
Why It Matters:
-
Reduces CO₂, NOₓ, and particulate matter emissions.
-
Cuts noise pollution near the docks.
-
Enhances port competitiveness by adhering to upcoming European green regulations.
The project is aligned with both Spain’s national decarbonization goals and the European Union’s Green Deal, which mandates that key ports provide shore power by 2030. By starting early, the Port of Bilbao is setting an example for other regional and international ports to follow.
Singapore: New Charging Station for Electric Vessels Signals Major Shift
In another major leap forward for maritime sustainability, Yinson GreenTech and Wilhelmsen Ships Service (WSS) have jointly unveiled a new charging station for electric vessels at WSS’s Singapore facility. This marks the first collaborative project between the two companies in the field of electric maritime mobility.
Notably, they’ve also partnered to build their first electric ship, a move that underscores their long-term vision of deploying electric vessel solutions across the commercial shipping sector. Singapore, a global shipping hub, has always played a pioneering role in maritime innovation, and this step further reinforces its commitment to clean energy adoption in one of the world’s busiest ports.
Key Benefits:
-
Faster charging capabilities for electric vessels.
-
Reduced turnaround times and operational costs.
-
Establishes Singapore as a hub for maritime electrification in Southeast Asia.
This development aligns with Singapore’s Maritime GreenFuture initiative, which focuses on digital transformation and environmental sustainability in port operations and vessel technology.
HAROPA PORT and BREEZE Project: EU-Backed Collaboration for Green Ports
In France, HAROPA PORT is making its own waves in the electrification space by joining the BREEZE project, a cross-European partnership with eight organizations committed to achieving shore power compliance with EU regulations by 2030.
BREEZE is part of the INTERREG Europe programme, which promotes collaborative solutions for regional growth, climate change adaptation, and digital innovation. HAROPA’s participation in this project reflects a strategic alignment with Europe’s aggressive carbon neutrality targets.
Objectives of the BREEZE Project:
-
Ensure shore power systems meet future regulatory standards.
-
Promote knowledge exchange and best practices across ports.
-
Accelerate the green transition of European maritime infrastructure.
As one of France’s largest port complexes (encompassing Le Havre, Rouen, and Paris), HAROPA PORT’s move is both symbolic and practical. It highlights the importance of joint regional efforts to scale up shore power availability, enhance interoperability, and reduce overall emissions from maritime operations.
Drivers Behind Port Electrification
Port electrification is no longer a theoretical concept—it is now a core element of global maritime strategies. A combination of factors is pushing ports toward sustainable energy adoption:
-
Stricter environmental regulations: The IMO and EU are introducing tighter emission standards for ships and ports.
-
Growing stakeholder pressure: Shipping customers and investors are demanding greener supply chains.
-
Technological readiness: Advancements in electric grid infrastructure, smart metering, and vessel battery technologies make shore power viable.
-
Incentives and funding: Governments and global institutions are providing grants, subsidies, and tax reliefs for green port initiatives.
Challenges to Overcome
Despite the momentum, several barriers remain in scaling port electrification globally:
-
High upfront costs for infrastructure deployment and retrofitting ships.
-
Grid capacity limitations in some older port cities.
-
Lack of universal technical standards for shore power connectors and systems.
-
Operational disruption during installation and testing phases.
Overcoming these hurdles will require continued investment, international collaboration, and a unified approach to regulatory compliance.
Opportunities and the Road Ahead
Port electrification presents a massive opportunity not just for emissions reduction but also for innovation in the maritime ecosystem. The integration of smart energy management systems, AI-driven grid optimization, and IoT-based monitoring could unlock higher efficiency and reliability in port operations.
Future possibilities include:
-
Integration with renewable energy sources like offshore wind and solar.
-
Development of battery swapping stations for short-haul electric ships.
-
Real-time energy analytics using AI and machine learning.
-
Cross-border port collaboration platforms for standardizing infrastructure rollout.
As more ports like Bilbao, Singapore, and HAROPA take bold steps, the global shipping industry edges closer to a net-zero emissions future.
What Is the Role of AI in Port Electrification?
Artificial Intelligence is playing a growing role in optimizing port electrification systems. Here’s how:
-
Energy Demand Forecasting: AI models help predict the energy needs of vessels and adjust grid supply accordingly, reducing wastage and ensuring grid stability.
-
Predictive Maintenance: AI-driven analytics identify wear and potential failures in electrical infrastructure before breakdowns occur, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
-
Smart Scheduling: AI optimizes when and where vessels connect to shore power based on traffic, power availability, and environmental impact.
-
Real-time Monitoring: IoT sensors and AI algorithms track power usage, emissions, and performance metrics, helping ports make data-driven decisions.
By integrating AI with electrification infrastructure, ports can unlock new levels of operational efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Conclusion
The global port electrification movement in 2025 marks a critical inflection point for the maritime industry. With leading projects from the Port of Bilbao, Singapore, and HAROPA PORT, the foundation is being laid for a cleaner, smarter, and more sustainable shipping future.
These pioneering efforts showcase how innovation, collaboration, and long-term vision can drive systemic change. As electrification scales across ports worldwide, the path toward carbon-neutral maritime transport is becoming not just a goal—but an attainable reality.
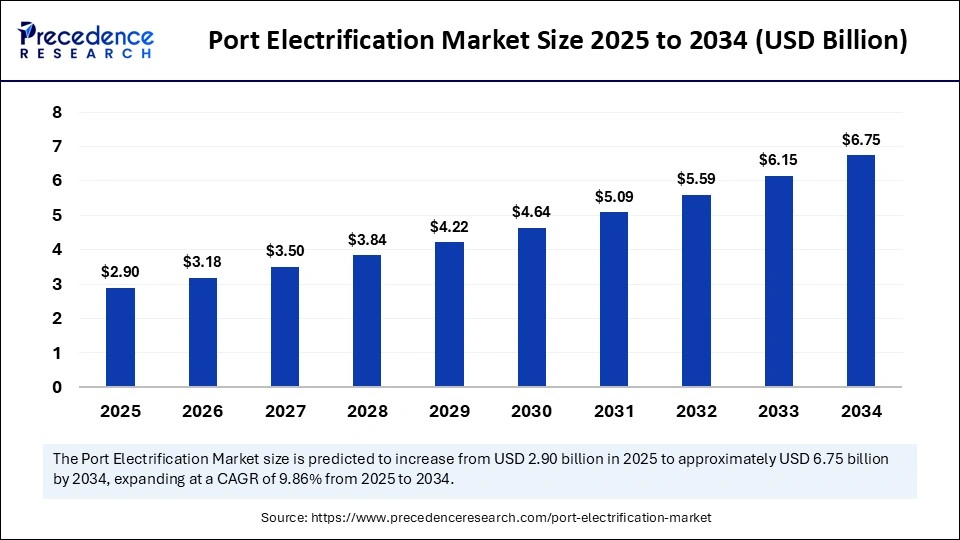
Also Read: Port Electrification Market
Source: Precedence Research